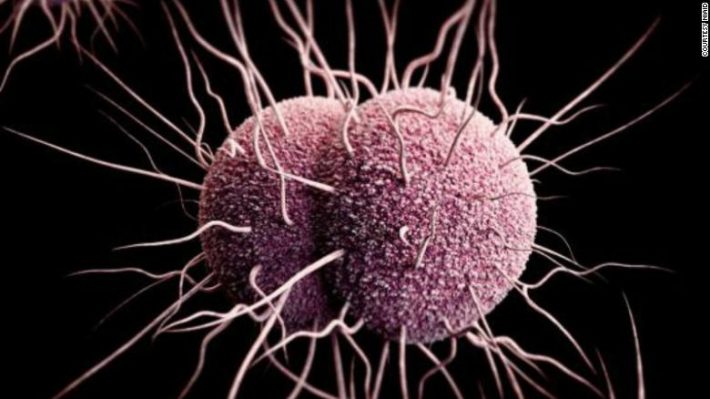
Gonorrhoea is a bacterial infection spread through unprotected sex, including oral sex. Initial symptoms, appearing around two to ten days after exposure, include painful urination, a discharge of pus from the penis or heavier than usual vaginal discharge. However, for many people, there are no symptoms.
Treatment
If you think you’ve been infected, go to a doctor to be tested. Gonorrhoea can usually be treated by a single dose of penicillin, though more resistant strains might require other antibiotics.
If you don’t get treated, and the bacteria remain in the system, there might be more serious long-term effects. Inflammation of the sexual organs might result. The Fallopian tubes might be closed, leading to infertility and, potentially, ectopic pregnancy. In very rare cases, gonorrhoea can spread through the veins to the whole body, resulting in aching joints, shivering, brain damage and inflammation of the heart.
It is relatively easily transmitted and, if you’ve got it, your sexual partner or partners should be tested too.