Temperature method
A method of predicting when ovulation occurs by taking a woman’s body temperature at the same time each day. Ovulation has occurred when body temperature has risen slightly for three days. See Natural methods.
Termination
See Abortion.
Testes or testicles
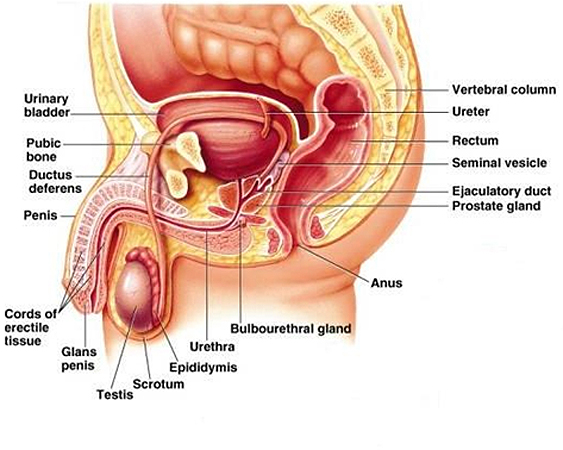
The two male sex glands or gonads located in the scrotum, which produce the male sex hormone testosterone and the reproductive cells, the sperm. Sperm are produced, matured and nourished in the long, narrow, tightly coiled seminiferous tubules within each testis, before being released into the epididymis where they are matured further and stored until needed. Sperm production is constant throughout most of the male’s mature life. The testes are equivalent to the ovaries in the female. See Seminiferous Tubules, Sperm.
Testosterone
A steroid hormone produced in the testes in the male and in other glands. Often described as a ‘male’ hormone, it is in fact produced in both males and females. In males, it causes the development of the sex organs in the foetus. At puberty it is responsible for the maturation of the sex organs and the development of the secondary sexual characteristics. In the adult it influences male and female sexual desire and male sexual performance. See Oestrogen.
Thai Beads
Sex aid consisting of plastic beads threaded onto a string or rod, inserted into the anus and moved in and out to enhance sexual arousal. See Sex aids, Sex toys.
Thrush
See Candida albicans.
Ticklers
Rubber or latex sheaths for the penis, which have bumps and knobs on them, either down the shaft or at the tip, to stimulate the clitoris, vagina and/or cervix. Ticklers are produced as sex aids, not contraceptives. See Clitoral stimulator.
Transgendered
A term used to describe a transsexual who has had a gender reassignment operation. See Gender reassignment.
Transsexualism
Condition where gender identity does not follow biological gender. See Gender identity, Gender reassignment.
Transvestism
Desired or habitual dressing in the clothing and/or under clothing associated with the opposite sex, sometimes with the appropriate make-up and accessories as well. Transvestites may be male or female and are usually heterosexual. In most cases the motivation behind transvestism is a form of fetishistic attraction to the clothing and accoutrements of the opposite sex, but it may also have to do with an attraction to the gender role of the opposite sex, symbolised by their clothes.
Tribadism
A primarily lesbian sexual practice in which one partner lies on top of the other and both move together to stimulate each other’s clitoris.
Trichomoniasis
A sexually transmitted disease caused by a small parasite that infects the vagina, causing inflammation and irritation. It can also spread to the cervix. Men are only rarely infected, in the urethra, where it can cause NGU.
Tricking
(1) Enjoyment of casual sex; a trick refers either to the casual encounter itself or to the partner in such an encounter. (2) Paid encounter secured by sex worker.
Troilism
Term used to describe three people having sex together, in any combination of male and female. See Ménage à trois.
Uncut
Term used to describe an uncircumcised penis.
Unprotected sex
Sexual activity that does not involve safer sex practices. These may lead to pregnancy or infection. See Condom, Contraception.
Urethra
The tube through which urine passes from the bladder; in men the urethra also carries semen during ejaculation. See Penis.
Urethritis
Inflammation of the urethra, usually caused by bacterial infection. See NGU.
Urolagnia
See Water sports.
Uterus or womb
The female reproductive organ in which an embryo grows, matures and is nourished. The uterus lies between the bladder and the rectum, where it is held in place by various ligaments. The main part of its wall is made up of muscle. The two fallopian tubes are attached on either side, linking it with the ovaries, while the cervix or neck of the uterus provides the passageway between the uterus and the vagina. The lining of the uterus is known as the endometrium, and is prepared each month for the implantation of a fertilized ovum as part of the menstrual cycle. See Menstrual Cycle, Cervix, Vagina.
Vacuum device
A sex aid designed to help a man achieve and maintain an erection. It is placed over the penis; air is pumped out and the vacuum created causes an erection. A tight band is placed around the base of the penis to maintain the erection and the device is removed.
Vagina
The passage between the vulva and the cervix. It is a fibro-muscular structure covered with a thin mucous membrane. The various layers of muscle – together with the numerous folds of skin by which they are covered – give the vagina great capacity for expansion and contraction. The smooth muscle within the vaginal wall is not under voluntary control and relaxes and stretches as necessary during sexual arousal, penile penetration and childbirth without conscious effort, while the muscle fibres surrounding the outer third of the vagina can usually be tensed and relaxed voluntarily. In the course of sexual arousal the vagina dilates and ‘sweats’ a lubricating substance from its walls. As the woman approaches orgasm the upper part of the vagina balloons and the outer part swells to form what is sometimes known as the ‘orgasmic platform’, on which the rhythmic muscle contractions of orgasm are focused.
Vaginismus
Condition in which the muscles around the outer third of the vagina contract very tightly making penetration painful, difficult or impossible.
Vaginitis
Inflammation of the vagina, caused by infection, injury or atrophy.
Vas deferens
The tube that conveys sperm from the testes to the penis, as part of the spermatic cord. See Testes.
Vasectomy
Surgical operation in which the vasa deferentia are cut and tied so that sperm cannot be passed along them and are therefore not released in the ejaculate. See Sterilization.
Vasocongestion
The process of tissue becoming engorged with blood, as when the penis becomes erect.
Venereal Disease (VD)
Any disease that can be transmitted by sexual contact, now more commonly termed Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs).
Vestibule
The area between a woman’s inner labia where the vaginal opening and the urethral opening are situated.
Vibrator
Sex aid, powered by mains electricity or batteries, that vibrates rhythmically to produce sensual pleasure. Vibrators are made in a great variety of shapes but the most common are those shaped as erect penises. Some have attachments for simultaneous stimulation of the clitoris, others for use in the anus; anal vibrators are also available. Vibrators are also made in the shape of vaginas. Vibrating devices are most frequently used for masturbation on or around the genitals but they may be used to stimulate any part of the body.
Virgin
Person who has never experienced sexual intercourse.
Voyeur
A person who enjoys and becomes sexually aroused by watching others undress or engage in sexual activities. See Peeping Tom.
Vulva
The external female genitalia.
Watersports (WS)
Sexual acts that involve one partner urinating over (golden shower) or into (golden screw) their partner.
Wet dream
See Nocturnal emission.
Wide-on
The state of advanced female sexual arousal that results in a relaxation of the vaginal muscles. It is analogous with the male hard-on.
Withdrawal
See Coitus interruptus.
Womb
See Uterus